We’re taught to glorify innovation. Every new invention is pitched as a step forward, a clever disruption, a mark of progress. But here’s the uncomfortable reality: not all innovation is good. Some of it is pointless, harmful, or simply stupid. Just because something can be invented doesn’t mean it should exist.
We don’t talk enough about bad innovation. The products that solve non-existent problems, the technologies that make products even worse.
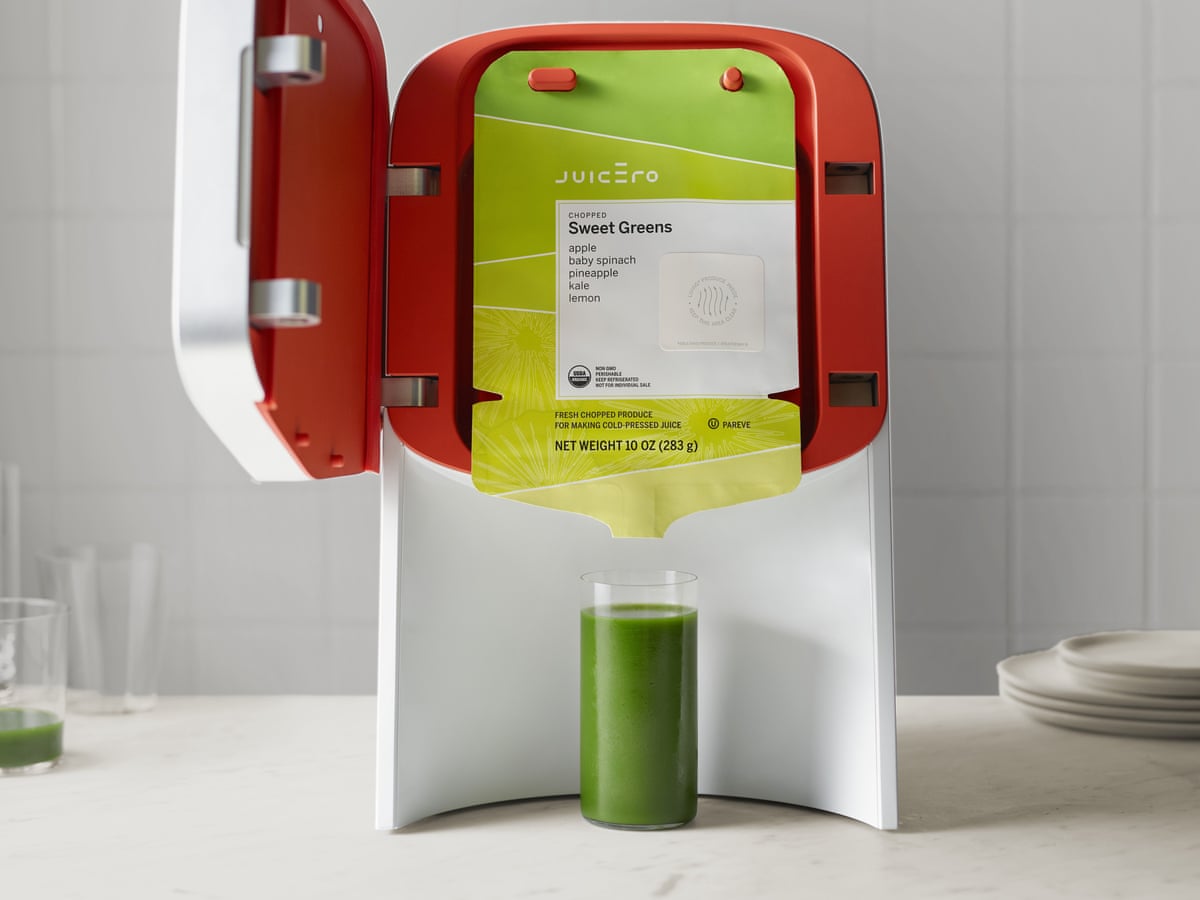
A $400 Wi-Fi juicer that squeezed juice packs you could already squeeze with your hands. A monument to Silicon Valley’s obsession with reinventing the obvious.

Sold as the future of wearable tech. Delivered as a creepy surveillance device nobody wanted to wear in public. A failure not just of design, but of common sense.

-
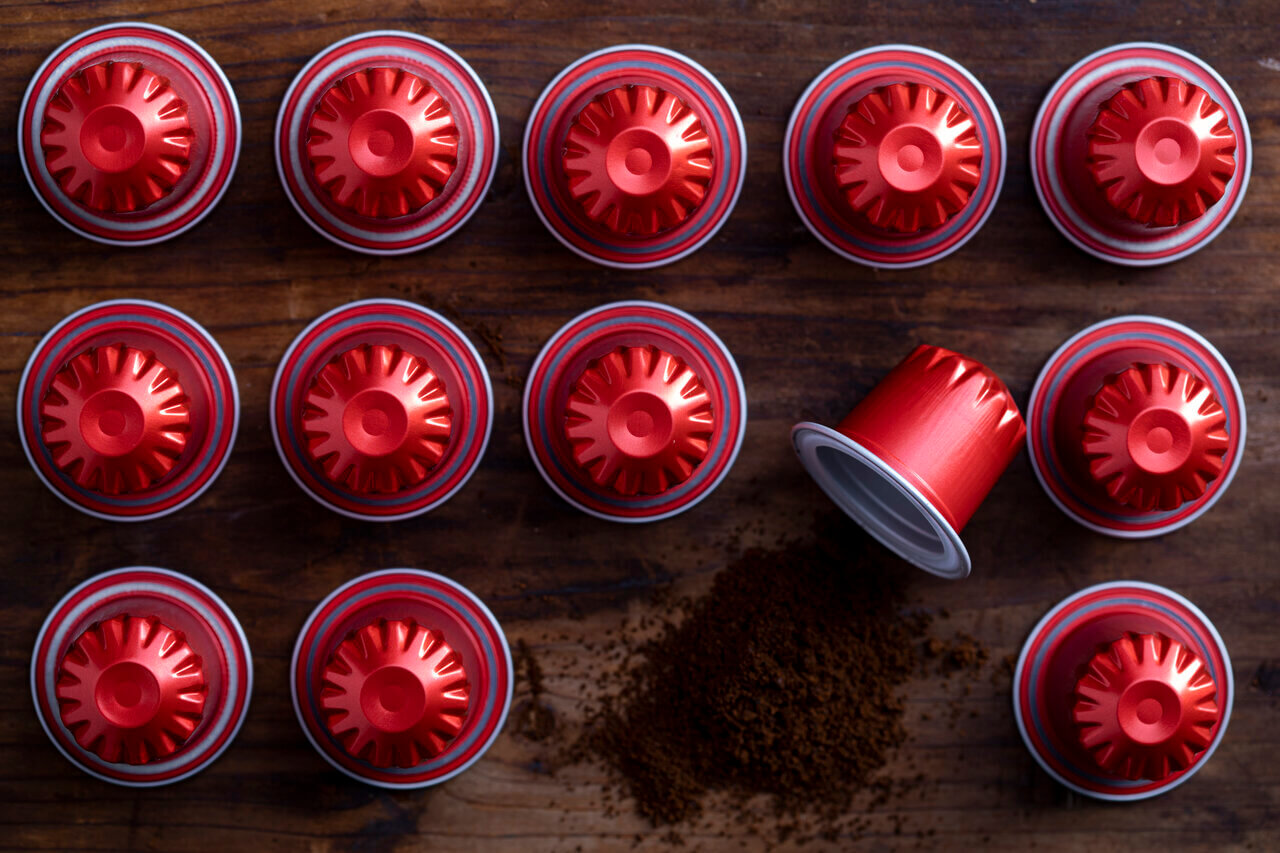
Plastic coffee pods
Convenient but extremely unnecessary. A brilliant way to turn convenience into global pollution.

-
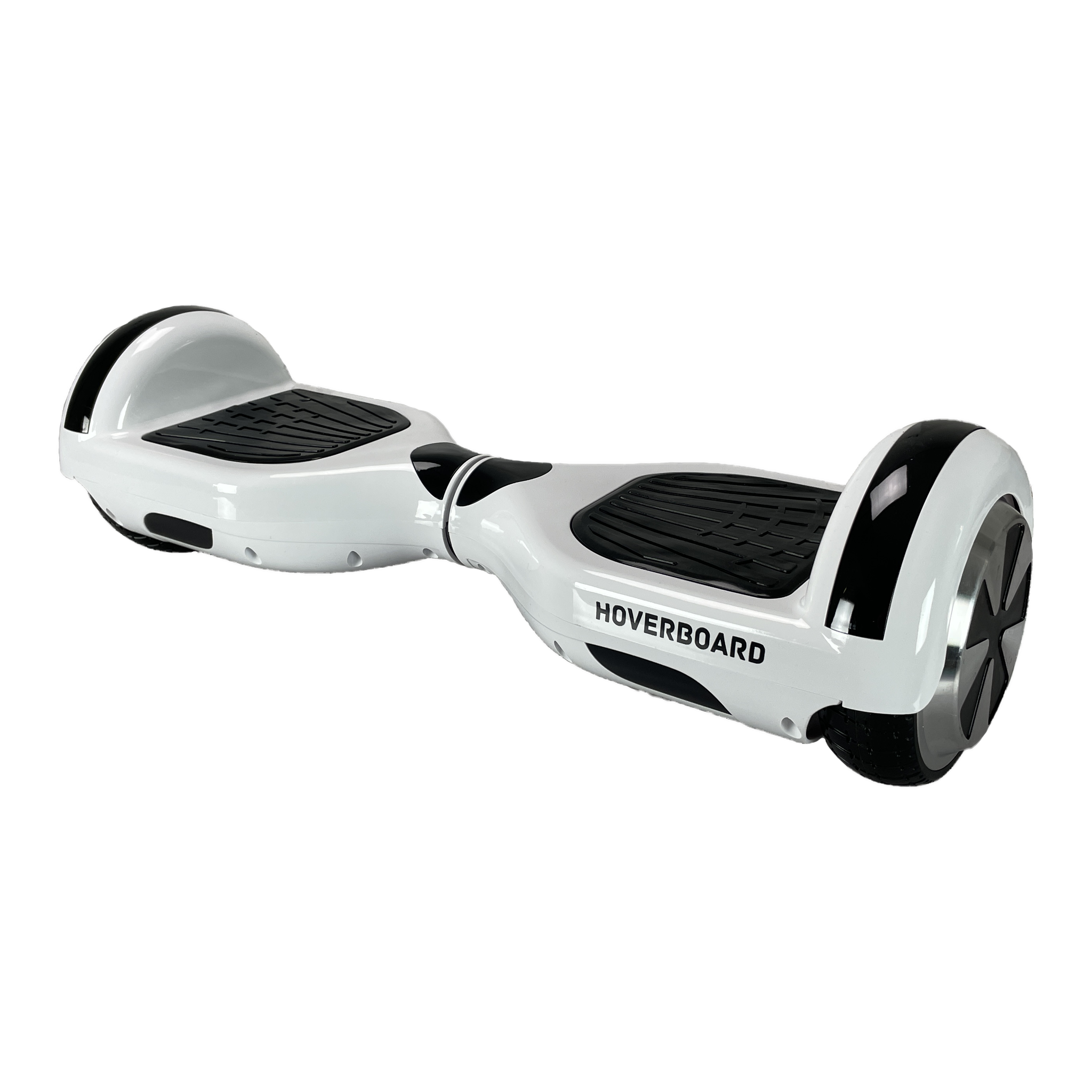
Hoverboards
Cheap self-balancing scooters that exploded (literally) because manufacturers raced ahead of safety.

-
Endless social media “features”
Are stories, reels, shorts, fleets, threads and endless copies of each other necessary? Innovation disguised as repetition, designed only to steal more of our attention.

-
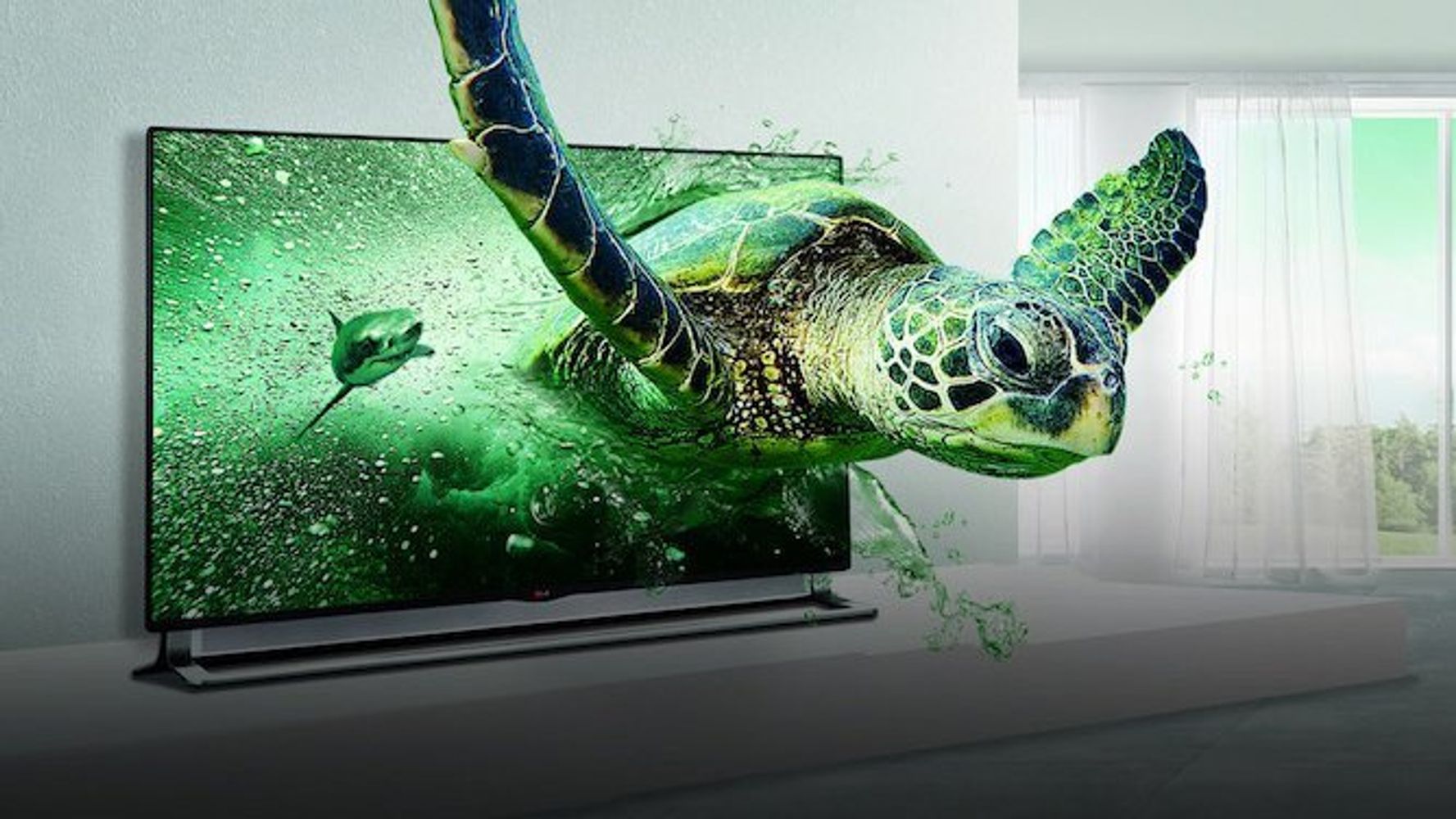
3D TVs
A stupid, useless gimmick that died almost as fast as it arrived.

-
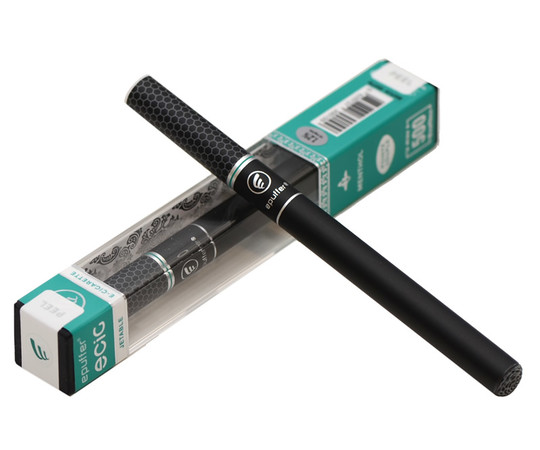
Disposable e-cigarettes
Marketed as a healthy alternative to smoking. In reality, they hooked a new generation on nicotine while creating mountains of toxic waste.

Innovation without purpose is just noise. Sometimes it’s laughable, a Wi-Fi toaster, sometimes it’s dangerous, vaping devices for teenagers, and sometimes it’s destructive, convenience products that poison ecosystems.
The real problem is that we confuse novelty with progress. We treat any new feature, any shiny object, any “world-changing” startup pitch as inherently valuable. Progress isn’t about making things new. It’s about making things better. And those two are not the same.


 Although democracy and innovation aren’t a perfect symbiotic pair, their relationship is deeply intertwined and they greatly depend on each other.
Although democracy and innovation aren’t a perfect symbiotic pair, their relationship is deeply intertwined and they greatly depend on each other.